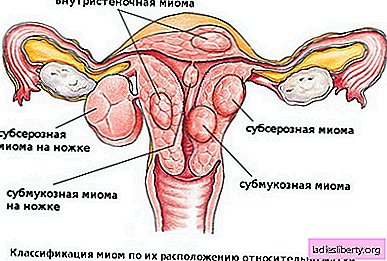
Uterine fibroids they call a benign hormone-dependent tumor in the muscle layer of the uterus in women of reproductive age. Mostly myomas affect women from 30 to 45 years old. In the total number of gynecological diseases, it is approximately 30%.
Myoma - reasons
There are currently no exact data on the causes of uterine fibroids. However, reliable it is known that this disease can develop in the presence of such factors:
- Ovarian diseases leading to impaired production of sex hormones;
- prolonged stress;
- heavy physical work;
- chronic infectious diseases (pyelonephritis, tonsillitis, etc.);
- diseases of the endocrine glands;
- obesity;
- bad heredity.
The growth of already appearing nodes of uterine fibroids can be caused by:
- abortion;
- the lack of a woman at 30 years of at least one pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the female genital area;
- long-term use of combined oral contraceptives;
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
Myoma - Symptoms
Usually, uterine fibroids, even large ones, have no particular symptoms and are detected by chance when examining a woman for another disease. However, in some cases, it may occur:
- heavy and prolonged bleeding during menstruation;
- irregular monthly or intermediate spotting from the vagina;
- prolonged, pulling pains in the lower abdomen;
- an increase in the circumference of the abdomen in the absence of a noticeable increase in body weight;
- a feeling of pressure in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urination, prolonged constipation;
- difficulties in conceiving a child.
However, a woman should remember that the above symptoms can indicate not only myoma, but also other diseases that are dangerous for a woman (cancer of the uterus or ovaries, endometriosis). Therefore, when they are detected, she must definitely consult a doctor.
Myoma - diagnosis
Diagnosis of uterine fibroids is based on data from a gynecological examination, ultrasound of the uterus and, if necessary, hysterography and hysteroscopy.
A gynecological examination is performed to detect an increase in the size of the uterus or an individual myoma node. Ultrasound of the uterus also allows you to verify the increase in the size of the uterus and makes it possible for early detection of the uterine myoma node, even with its size not exceeding 1 cm in diameter. Hysterography is carried out in case of difficulty in diagnosing uterine fibroids, by introducing a contrast agent into the uterine cavity with subsequent radiography. With hysteroscopy, a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity - a special device that allows the doctor to see its cavity.
Myoma - treatment and prevention
For the treatment of uterine fibroids, as a rule, conservative treatment with anti-inflammatory, restorative drugs and sedatives is provided. A good effect in the treatment can be achieved by taking vegetable juices and decoctions of herbs, however, they must also be prescribed by a doctor.
Surgical treatment of uterine fibroids is carried out in the case of:
- rapid growth of fibroids;
- its large size;
- menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding;
- anemia;
- submucosal location of the myomatous node, which is the reason for the high risk of developing profuse bleeding;
- suspicion of malignant degeneration.
The volume of surgery is determined by the age of the woman (since maintaining her reproductive function requires organ-preserving surgery, in which only the node is removed), concomitant diseases, and the presence of life-threatening complications.