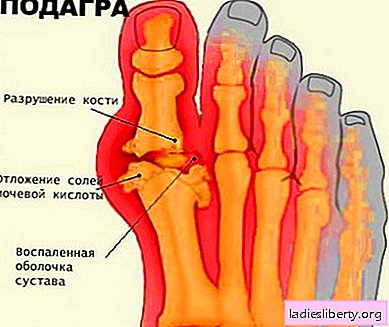
Gout - a disease that in typical cases causes painful swelling of the joints. It is characterized by a sharp increase in the level of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia) and deposition of sodium urate (acid salts) in the tissues of the body. Such deposits in the joints, mainly in the joints of the fingers and toes, cause extremely painful and severe inflammation.
Most forms of gout are hereditary. The disease is usually observed in women after menopause and in men after 40 years. Gout is manifested by sudden and rather intense pain, “heat” and redness in the joint. As a rule, attacks of gout occur at night against the background of overeating or drinking alcohol. A second attack is preceded by tingling in the affected joint. If the disease is not treated, periods of exacerbation become longer, and seizures more often. Arthritis affects new joints, often urinary tract and kidneys suffer.
Gout - Reasons
Gout is caused by the accumulation of uric acid in the tissues of the body. Its excess occurs for two reasons. In one form of the disease, the kidneys cannot excrete uric acid, which is produced in normal amounts. The second form is when the uric acid formed in the body exceeds the ability of the kidneys to excrete it.
Some patients suffering from the second form of gout have a congenital metabolic defect (the absence of a key enzyme) that reduces the formation of uric acid in the body. Excess uric acid is also an indirect consequence of conditions that are associated with metabolic disorders (pernicious anemia, medication, or starvation). Gout, developing in such cases, is called secondary.
Gout - Symptoms
Gout is manifested by sudden, rapid pain, which peaks in literally several hours. Seizures usually occur early in the morning or at night. Almost instantaneous swelling of the joint and its redness occurs, the patient complains of fever and “heat” in the bones. The affected joint loses mobility and the person feels unbearable pain even from the lightest touch.
First of all, a small joint located on the foot at the base of the thumb is subjected to gouty attack. The pain syndrome lasts, as a rule, from 2 hours to several days. Over time, attacks become more common, arthritis spreads to new joints, there is a chance of damage to the urinary tract and kidneys with the formation of stones.
Gout - Diagnosis
Gout is difficult to recognize and distinguish from other joint diseases. Diagnosis is based on visual inspection, studying the history and analysis of blood for uric acid content. The main test for gout is arthrocentesis (articular aspiration), which allows the detection of uric acid salts. To diagnose gout, X-rays are often prescribed to detect tofus formations around the joints and determine the stage of bone damage.
Gout - treatment and prevention
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely recover from gout. However, it’s quite possible to control the seizures of the disease using the right diet. Of the drugs for exacerbation of gout, anti-inflammatory drugs (colchicine, indomethacin, phenylbutazone) and painkillers, as well as drugs that slow the formation of uric acid, are used. Sometimes a doctor may prescribe corticosteroid hormones (Triamcinolone, Hexacetonide), which change the acidity of the urine.
Modern medicine uses a blood purification procedure to relieve gout attacks, using special devices (plasmophoresis hemosorption). All treatment methods include weight correction of the patient and a special diet.
Gout prophylaxis involves regular monitoring of uric acid levels. It is very important to adhere to a healthy lifestyle. It must be remembered that gout occurs in people with high blood pressure and overweight. Eating a diet with the restriction of purine-rich foods is crucial in preventing gout.